Understanding the Different Types of Collagen and Their Benefits
Collagen is often hailed as the secret to youthful skin, strong joints, and a healthy gut. As the most abundant protein in the human body, collagen forms the structural foundation of our skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. But not all collagen is created equal—there are at least 28 different types, with five being the most relevant to health and wellness. Among those, Types I, II, III, V, and X are the most commonly found in supplements.
If you’ve ever stood in the supplement aisle feeling overwhelmed by all the collagen options—hydrolyzed, marine, Type I, II, III—this guide is for you. Let’s break it down.
1. Type I Collagen – The Skin, Hair & Nails Booster
Source: Bovine (cow), marine (fish)
Found In: Skin, tendons, bones, ligaments
Benefits:
Improves skin elasticity and hydration
Strengthens hair and nails
Supports bone density
Promotes wound healing
Best For: Beauty and anti-aging purposes. Type I is the most abundant form in the body and makes up about 90% of your skin’s collagen.
Popular Form: Hydrolyzed collagen peptides (easily absorbed by the body)
2. Type II Collagen – The Joint and Cartilage Healer
Source: Chicken cartilage (particularly from the sternum)
Found In: Cartilage
Benefits:
Supports joint health and mobility
Reduces joint pain and inflammation
Helps rebuild cartilage
Best For: People with joint conditions like arthritis or athletes who want to protect their joints.
Popular Form: Undenatured type II collagen (UC-II) is a common supplement form that is not broken down into peptides, which may allow it to stimulate cartilage repair more effectively.
3. Type III Collagen – The Skin and Organ Supporter
Source: Bovine (cow)
Found In: Skin, lungs, blood vessels, and internal organs
Benefits:
Supports skin structure and elasticity
Promotes gut lining integrity
Helps in cardiovascular health
Best For: Often paired with Type I for beauty and gut health. It’s the second most abundant collagen in the human body.
Popular Form: Often found alongside Type I in hydrolyzed collagen supplements.
4. Type V Collagen – The Eye and Placenta Protector
Source: Eggs, especially eggshell membranes
Found In: Cornea of the eyes, hair, placenta
Benefits:
Supports eye health
Important in the formation of cell membranes
Helps regulate collagen fibril size (i.e., makes other collagen types more effective)
Best For: Those interested in overall cellular function, fertility support, and eye care.
5. Type X Collagen – The Bone Builder
Source: Chicken and eggshell membranes
Found In: Cartilage at growth plates, joints
Benefits:
Supports new bone formation
Helps repair joint injuries
Aids in healing fractures
Best For: Bone healing, post-injury recovery, and advanced joint care.
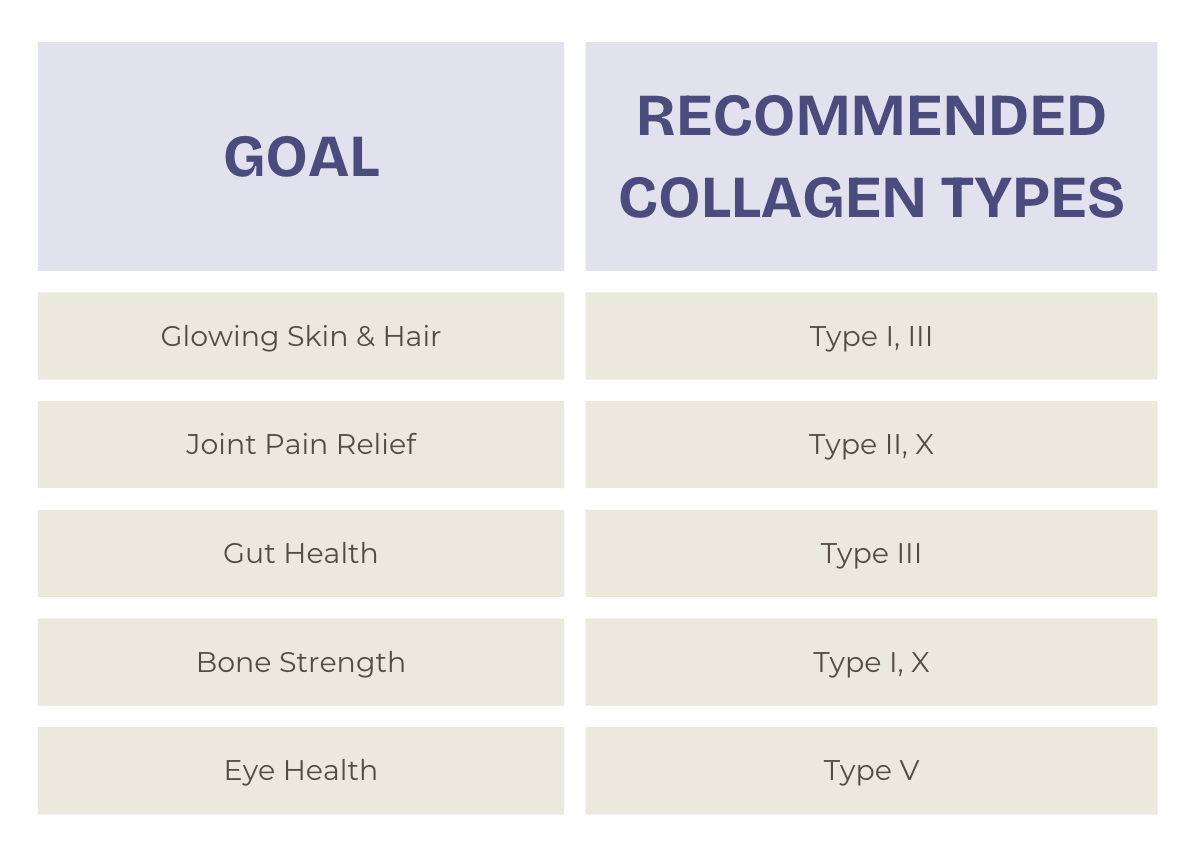
Choosing the Right Collagen for You
When shopping for collagen supplements, consider your health goals:
Also, pay attention to the form of collagen:
Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides: Easily absorbed; most common form.
Undenatured Collagen: Preserves protein structure; may be better for immune-related joint benefits.
Gelatin: Less processed, forms a gel; great for cooking.
Great Collagen Finds on Amazon:
FTC Disclaimer: Some links in this guide may be affiliate links. If you purchase a product with the links that I provide I may receive a small commission. There is no additional charge to you!Adding collagen to your wellness routine can be a game changer, whether you’re looking to smooth wrinkles, ease joint discomfort, or strengthen your gut. The key is to match the right type of collagen to your needs—and stick with it consistently. Most people begin to see results in 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the goal.
As always, consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying conditions or allergies (particularly to fish, eggs, or chicken).
Want a deeper dive into pros and cons of these collagen brands or how to mix collagen into your daily routine? Drop a comment or question below!